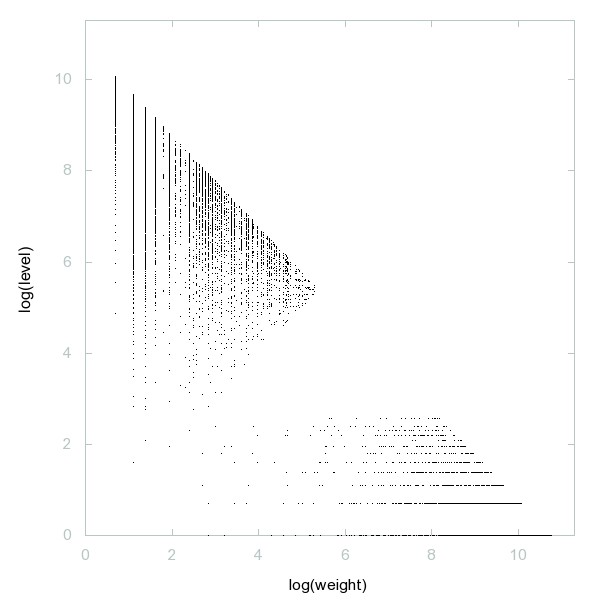
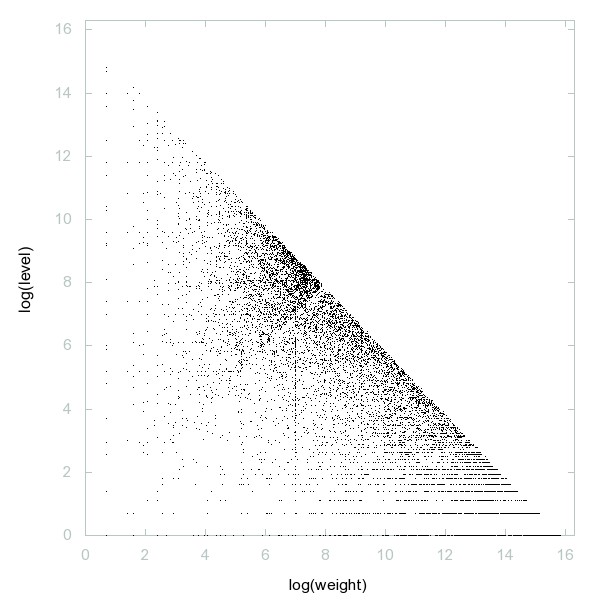
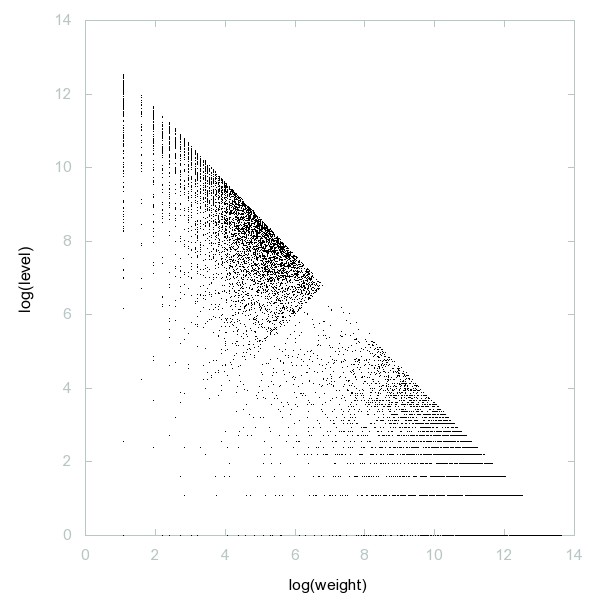
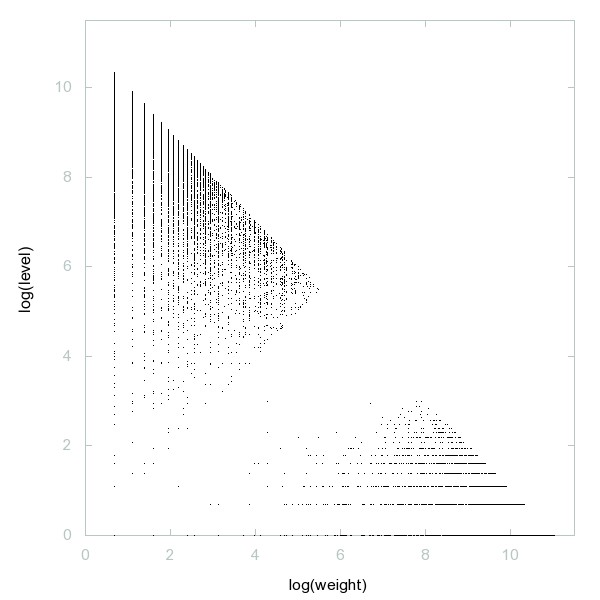
Decomposition of A230634
Numbers n such that m + (sum of digits in base-4 representation of m) = n has exactly two solutions.
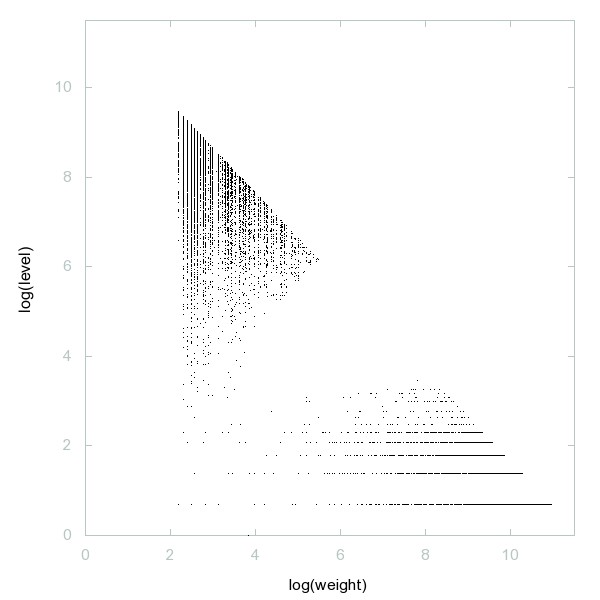
Decomposition of A230853
Numbers n such that m + (sum of digits in base-3 representation of m) = n has exactly one solution.
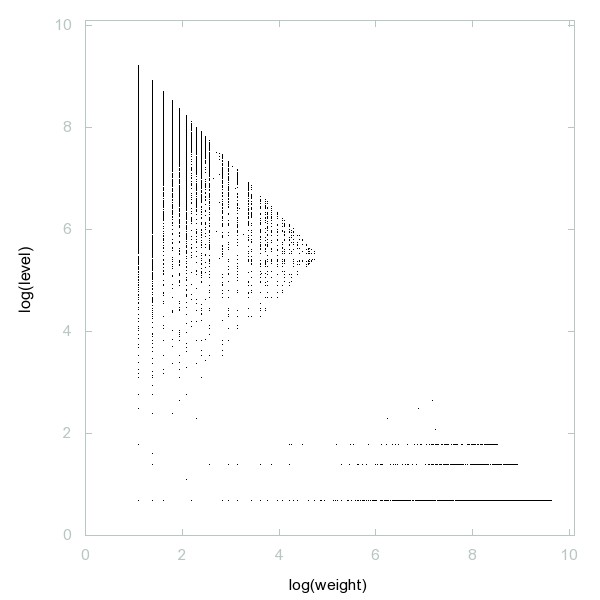
Decomposition of A230854
Numbers n such that m + (sum of digits in base-3 representation of m) = n has exactly two solutions.
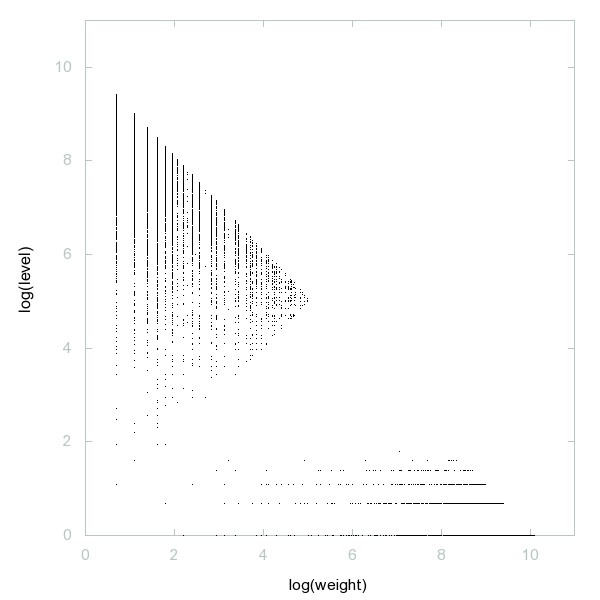
Decomposition of A232054
Complement of A056875.
Decomposition of A233010
In balanced ternary notation, either a palindrome or becomes a palindrome if trailing 0's are omitted.
Decomposition of A234695
Primes p with prime(p) - p + 1 also prime.
Decomposition of A235033
Numbers which are factored to a different set of primes in Z as to the irreducible polynomials in GF(2)[X].
Decomposition of A235034
Numbers whose prime divisors, when multiplied together without carry-bits (as encodings of GF(2)[X]-polynomials, with A048720), produce the original number; numbers for which A234741(n) = n.
Decomposition of A235035
Numbers n for which A234742(n) = n: numbers n whose binary representation encodes a GF(2)[X]-polynomial such that when its irreducible factors are multiplied together as ordinary integers (with carry-bits), the result is n.
Decomposition of A235592
Numbers k such that k*(k+1) - prime(k) is prime.